A mass of water was measured than poured into the calorimeter the water remained there until it reached room temperature.
Specific heat of water at room temperature approximately is.
The specific heat capacity of water vapour at room temperature is also higher than most other materials.
Since specific heat capacity does not depend on the object in question only the substance from which it is made specific heat capacities are much more useful.
The specific heat capacity of water is 4 200 joules per kilogram per degree celsius j kg c.
You need to look up the specific heat values c for aluminum and water.
The specific heat capacity c p of liquid water at room temperature and pressure is approximately 4 2 j g c.
As with most liquids the temperature of water increases as it absorbs heat and decreases as it releases heat.
This means it takes 4 2 joules of energy to raise 1 gram or 1 milliliter if you d rather think of the equivalent volume of 1 gram of water of water by 1 degree celsius.
Water is one of the latter it has a high specific heat capacity because it requires more energy to raise the temperature.
Water has a specific heat capacity of 4182 j kg c.
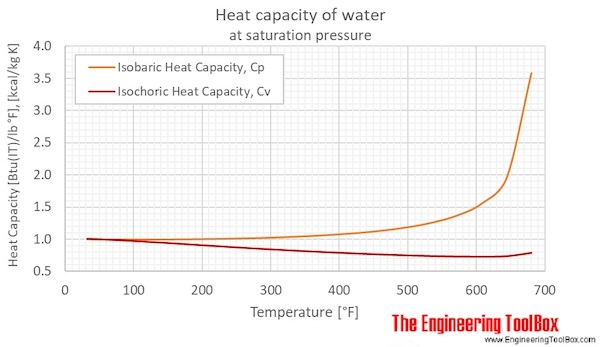
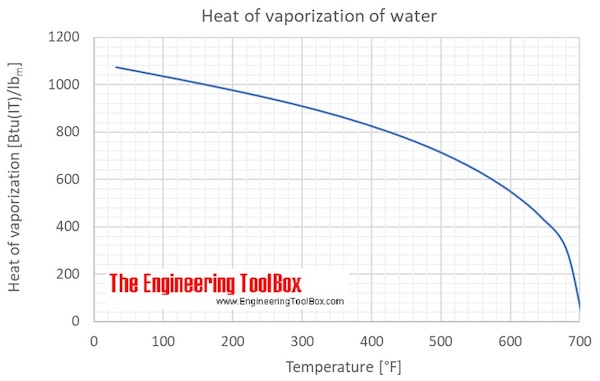
Water specific heat online calculator figures and tables showing specific heat of liquid water at constant volume or constant pressure at temperatures from 0 to 360 c 32 700 f si and imperial units.
Informally it is the amount of energy that must be added in the form of heat to one unit of mass of the substance in order to cause an increase of one unit in its temperature the si unit of specific heat is joule per kelvin and kilogram j k kg.
Because water is such an important and common substance we even have a special way to identify the amount of energy it takes to raise one gram of water by one degree.
The specific heat capacity symbol c p of a substance is the heat capacity of a sample of the substance divided by the mass of the sample.
This means that it takes 4 200 j to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water by 1 c.
For water vapour at room temperature and pressure the value of specific heat capacity cp is approximately 1 9 j g c.
A brief summary of the procedure is outlined below.
We will consider the specific heat capacity of the water to be known 1 00 kcal kg k.
Again you use q mcδt except you assume q aluminum q water and solve for t which is the final temperature.
Generally the most constant parameter is notably the volumetric heat capacity at least for solids which is notably around the value of 3 megajoule per cubic meter and kelvin.
The procedure for this experiment is thoroughly covered in the coinciding specific heat test article.
The following table of specific heat capacities gives the volumetric heat capacity as well as the specific heat capacity of some substances and engineering materials and when applicable the molar heat capacity.